HURIDAC
West Africa Human Rights Treaties Database
West African Human Rights Treaties
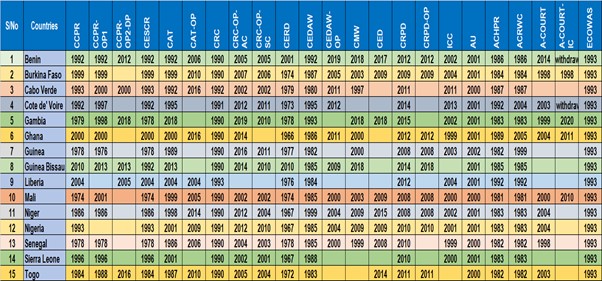
Human Rights Treaties Ratification is the act of signing a treaty by making it enforceable; it also refers to an act in which a state consents to be bound by a treaty. A treaty is an international agreement in which a state agrees to be governed by international law. This chapter will seek to examine the status of compliance of West African member countries that are signed to the core Human rights treaties.
A country becomes a party to a convention or treaty by signing and ratifying an instrument or by acceding to them. The first process of becoming a party is by signing the treaty. The status of a treaty is usually characterized by two listings. The status will either indicate that the state has a signatory or a party to a treaty.
UN Treaties
The United Nations (UN) is the custodian of almost all international treaties, while regional organizations such as the African Union, Council of Europe, and Organization of American States (OAS) administer the regional treaties. United Nations International instruments come in two forms, treaty-based instruments (covenant, charter, convention) and non-treaty-based instruments (declaration, code of conduct, principle, The process of being a state party to a treaty starts by being a signatory to the treaty but it doesn’t end with that; there are four different processes that a state adopts in this regard. The first is Ratification – a process of becoming a state party after signing a treaty. Second is Accession, which means that after the expiration of the deadline for signing a treaty or expiration of a limited number of deposited ratification instruments. Third, is Succession, which is the only option for a new state that wants to inherit the status or responsibility of a former state through succession to a treaty. Domestication is the fourth one; it a process of incorporating international treaties into local laws.
International Criminal Court
The Rome statute was adopted by the United Nations Diplomatic conference of plenipotentiaries and comes in force in July 2002;The ICC is an intergovernmental organisation and international tribunal that sits in the Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to persecute individuals for the international crimes of genocide, crime against humanity, war crime and the crime of aggression, it is intended to completed existing national Judicial systems and it may therefore exercise it jurisdiction only when national courts are unwilling or unable to persecute criminals .The ICC lacks universal territorial jurisdiction and may only investigate and persecute Crime committed within member states , crimes committed by nationals of member states or crimes referred by united Nations security Council.
AU Treaties
The African Union is the continental body of all states in Africa. It was established with the Constitutive Act of the African Union, 2000 and the Protocol to the Act (2003). The African Union Vision is read thus “An integrated, prosperous and peaceful Africa, driven by its citizens and representing a dynoamic force in the global arena”. There are specialised four(4) Technical committees, that handle (a) Justice and legal affairs, (b) Agriculture, Rural Development, Water and Environment, (c) Gender Equality and Women’s Empowerment, (d) Migration, Refugees and Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs).

The African Commission on Human and Peoples' Rights

The African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights (ACHPR) is a quasi-judicial body tasked with promoting and protecting human rights throughout the African continent as well as interpreting the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights and considering individual complaints of violations of the Charter, not excluding investigating human rights violations, creating and approving programs of action towards encouraging human rights, and set up effective communication between them and states to get first-hand information on violations of human rights. The Commission consists of 11 members elected by the AU Assembly from experts nominated by the state parties to the Charter. The Commission elects its Chairperson and Vice-Chairperson as the Bureau of the Commission. They are elected for a term of two years and are eligible for re-election once. The Bureau coordinates the activities of the Commission and supervises and assesses the work of the Commission’s Secretariat.)
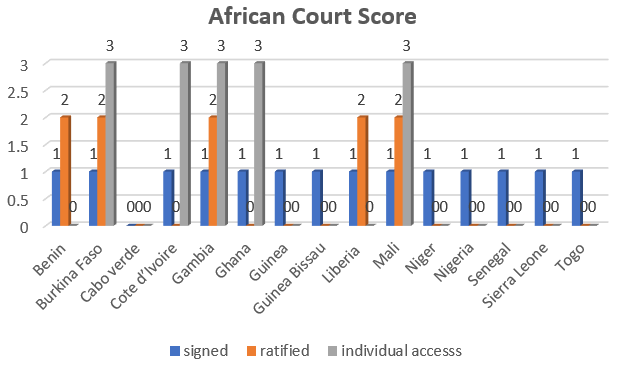
African Court
In regards to the protocol to the African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights, countries are scored as follows; signing the protocol is a point, ratifying it is two points and acceptance of individual access is three points. If a country withdraws an individual to access, such country is back to two points like the Benin Republic.


ECOWAS
The Economic Community of West Africa States Treaty is a multilateral agreement signed by member states that made up the ECOWAS ; The Treaty further takes into consideration the African charter on human and peoples rights and the declaration of political principles of the ECOWAS adopted in Abuja by the fourteen(14) ordinary session of the authority of Heads of state and government on 6 July 1991 and were further convinced that the integration of the integration of the member states into a viable regional community may demand the partial and gradually pooling of national sovereignty to the community within the context of collective political will. The ECOWAS community Treaty is focused on political and Economic Union however Human rights priority was highlighted in it too.