thematic dashboard
West African Human Rights Thematic Issues Dashboard
This section explores cases on Human Rights Thematic Focus Areas. The first section of the chapter will start with the issues concerning rights to electoral governance, access, and responsibilities of citizens; to electoral and public freedom as enshrined in treaties by International Human Rights organizations such as ICCPR, ICESCR, CEDAW, ACDEG, and CERD.
It will also highlight what it entails for elections to be termed free and fair. It climaxes on critical issues and challenges facing West Africa on a country-by-country basis with highlights to elections (recent violations and bitter experiences) and the right to vote
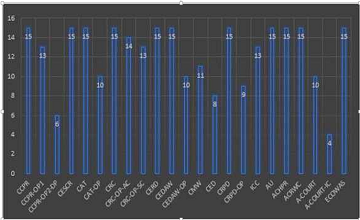
Countries Human Rights Ranking
United Nations International instruments come in two forms, treaty-based instruments (covenant, charter, convention) and non-treaty-based instruments (declaration, code of conduct, principles). A working relationship between a treaty and a state makes it (the treaty) effective. The relationship can be established by either being a signatory to a treaty or a state party to it. Being a signatory to a treaty means signing the treaty, which implies that a state binds itself to not do anything that will defeat the object and purpose of the treaty, pending the decision whether to ratify it.
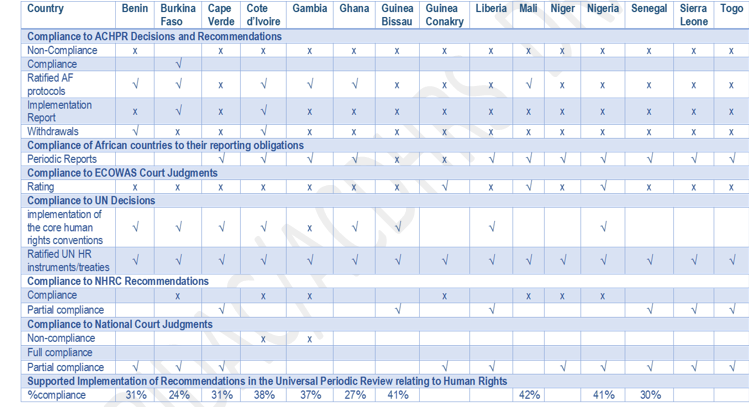
Countries Human Rights Compliance Gap
The UPR is deemed particularly strong in generating peer and public pressure on states.To build upon theoretical conditions of compliance,enforcement,management and constructivism.
The underlying principles of universality,cooperation and dialogue that guide the review have given states within the west African sub-region a renewal sense of engagement with the international Human Rights Institutions.The compliance levels thus far is below average depicting the need for more work to be done so as to complement national ,regional and international Human Rights mechanisms to improve the Human Rights situation on ground in West Africa.
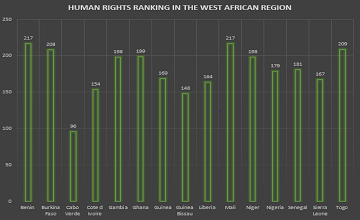
Human Rights and Insecurity
The nature of violence has changed significantly in West Africa since independence . This transformation was well articulated in the work of Bank T W. ‘The Challenge of Stability and Security in West Africa’.
He opined that : “The vast majority of armed conflicts in West Africa since independence have been intrastate conflicts, marked by 5 large-scale civil wars. In the new millennium, the incidence of civil wars and large-scale conflicts dropped off dramatically, representing a watershed in the political stabilization of the region. However, other forms of political violence and new threats have emerged such as election-related violence, longstanding ethno national conflict, drug trafficking, maritime piracy, and extremism” . He further affirmed that there are other stressors, which include youth inclusion, migration, the rapid development of extractive industries, and land management.
Human Rights and Corruption
This section heavily relied on arguments by various authors; excerpts from the book of one of the leading anti-corruption experts in Nigeria were also useful. Corruption is as old as humanity, yet international recognition of its corrosive nature is relatively recent. The fight against corruption is now an important aspect of contemporary international law. The last three decades have witnessed steady and even remarkable advances in recognizing corruption as an international problem that precipitates poverty and threatens both the rule of law and the foundation of a law-based state.
An impressive array of international conventions, declarations, guidelines national laws, and institutions exist to combat corruption and to establish a framework for international cooperation and assistance, in particular in the area of asset recovery . Intergovernmental organizations are constantly engaged in the fight against corruption and are issuing recommendations, directives, and codes of conduct, or more significantly, drafting legally binding international conventions.
Democratic Rights
The United Nations, custodian of most International human rights treaties has been examining this link in many rigorous processes. They believe that the Rule of law should be posited effectively by drawing the link between democracy and human rights. They describe this link as: “Democracy is one of the universal core values and principles of the United Nations. Respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms and the principle of holding periodic and genuine elections by universal suffrage are essential elements of democracy. These values are embodied in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and further developed in the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights which enshrines a host of political rights and civil liberties underpinning meaningful democracies. The rights enshrined in the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights and subsequent human rights instruments covering group rights (e.g. indigenous peoples, minorities, persons with disabilities), are equally essential for democracy as they ensure an equitable distribution of wealth, and equality and equity in respect of access to civil and political rights”
Covid-19 and Human Rights
This chapter focuses on the human rights perspective of the COVID-19 pandemic in West Africa.The sudden emergence of the new Coronavirus called COVID-19 has posed a political-economic challenge for governments in West Africa. These responses required governments to stop the spread of a virus that kills thousands. At the point of drafting this report, the novel Coronavirus (NCoV) has already killed over 2,473,879 people globally and infected 22,301,8741.
The government’s response in managing this crisis involves encroaching on the human rights space. Hence, human rights examination of the coronavirus pandemic is crucial to developing models for protecting the human rights of citizens during the COVID-19 pandemic. It explores the epidemiology and implications of the coronavirus, including the meaning of Coronavirus, its origin, preventive measures as well as other viruses that have invaded human history and their similarities and differences with Coronavirus
Women and Child's Rights
People Living with Disabilities
The Economic Community of West Africa States Treaty is a multilateral agreement signed by member states that made up the ECOWAS ; The Treaty further takes into consideration the African charter on human and peoples rights and the declaration of political principles of the ECOWAS adopted in Abuja by the fourteen(14) ordinary session of the authority of Heads of state and government on 6 July 1991 and were further convinced that the integration of the integration of the member states into a viable regional community may demand the partial and gradually pooling of national sovereignty to the community within the context of collective political will. The ECOWAS community Treaty is focused on political and Economic Union however Human rights priority was highlighted in it too.